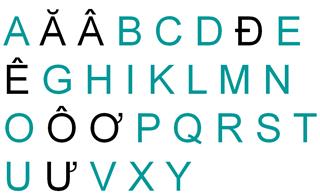Based on the relations between languages, the history of Vietnamese language is divided into six periods: Proto-Vietic language, pre-ancient Vietnamese, ancient Vietnamese, medieval Vietnamese, pre-modern Vietnamese, and modern Vietnamese.
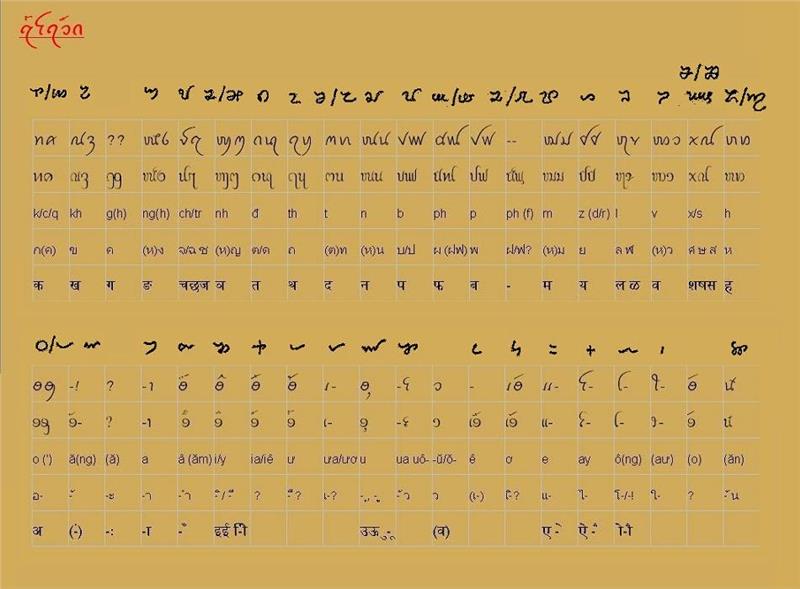
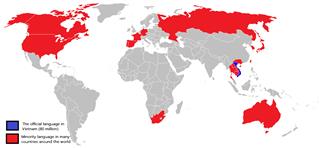
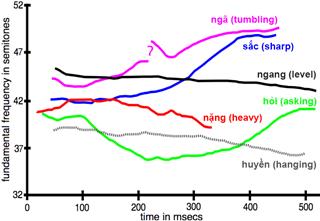
Vietnamese language is the official language of Vietnam. It is a language of the native origin. This language came into being in the agricultural civilization in the north of Red River and Ma River (Vietnam). According to the explanation of A. G. Haudricourt in 1954, Viet – Muong in early AD included languages and local language without diacritics. So far, through communicating with Chinese languages, especially the language belonging to Tai-Kadai, which has the high development of tones system, the system of tones in Vietnamese language appeared and had identifications as today. The appearance of tones formed in the 6th century (the Chinese domination of Vietnam) with three tones, and stably developed in the 12th century (Ly Dynasty) with 6 tones. Then, some of consonants changed so far. In the process of change, some final consonants disappeared, which made the change in ending syllables and consonants.

The history of Vietnamese language is being studied by linguistic community. In recent study, Vietnamese language originated from Viet – Muong which contains Vietnamese and Muong languages. Viet – Muong is the subdivisions of Vietic languages group, sub-branch of Austroasiatic language family. In Vietic languages group, apart from Viet – Muong language which are spoken in Son La, Thanh Hoa, and Nghe An, Nguon language is also seen as the closest language to Vietnamese language. The official language of Vietnamese people also has relation with some languages such as Chut, Pong, Ahoe, Maleng, and Thaveung which belong to Pong Chut language group. Some others believe that the Viet – Muong languages were not divided from Mon-Khmer languages, but Proto Vieto-Katuic languages, which occurred 4000 years ago. People who spoke Vietic languages resided in mountainous areas from Ha Tinh, Quang Binh, and Quang Tri to the middle of Laos. Since then, a number of them fled to the north of Vietnam and lived in the highland of Nghe An, Thanh Hoa, Hoa Binh, and Son La. Then, they communicated with northern people who spoke the language of Tai-Kadai (ancestors of Tay, Nung ethnic minority groups). The rest of population staying at their hometown remained Vietic languages and communicated with Katu, Bana, Khmer ethnic minority peoples. The interaction in the north was quite profound, which created an integration of many physical and mental traditions and cultures. People who spoke Viet – Muong language did not follow all features of Mon-Khmer languages, they communicated with people speaking Tai-Kadai and absorbed from them to develop Viet – Muong language strongly. Later, a large number of Viet – Muong residents left northern mountainous areas for plain areas to produce and develop in Red River Delta. That is a condition to form the cradle of Kinh people.

According to Vietnamese language studies, Vietnamese language was influenced by southern Chinese language, and French. The exposure to Han people, Han language and Han culture happened before Chinese annexing. However, the 1000-year Chinese domination left the most profound influence in Vietnam. The impact of Chinese culture and language did not expand widely and evenly in the dominated areas from mountainous to plain areas, and from the north to the south. Thus, the differences between Pong Chut and Viet-Muong became clear, and then they divided into two different languages from 2000 to 2500 years ago. Then, Viet – Muong languages was divided into Vietnamese language (in Red River Delta) - the pre-ancient Vietnamese language, and Muong language in Hoa Binh, Son La, and Phu Tho. This division took place about 1500 years ago. Since 939, Vietnam regained its autonomy; Chinese language did not directly affect in Vietnam. Even though, Vietnamese feudal dynasties remained using Chinese, and regarded it as an official writing system in all documents, organizations of education and examination in Chinese language became popular, but the language was no longer living language.
When Vietnam gained its autonomy, Vietnamese people created “Nom” characters based on rules of Chinese language to record what they spoke. Since then, Vietnamese language became important and rapidly developed. Although Vietnamese language was not used in official documents, education and examination, it became the most powerful language in the entire territory of Vietnam. The effect of Vietnamese started to spread widely in minority language areas, from the north to the south. This is the period of ancient Vietnamese language.

The formation of present-day Vietnamese alphabet was related to the mission of Western missionaries. Vietnamese alphabet is a type of language formed in accordance with recording by Latin alphabets which was used in Europe for a long time ago. By the 17th century, it was the phase of the medieval Vietnamese language. Some Western Catholics and Protesters applied the rule of Latin alphabets for recording Vietnamese language to create a convenient language to the purpose of promulgating their religion. In the following centuries, Vietnamese alphabets were only used in Christian bibles. The French colonialism resulted in the abolition of education, examination, and using Chinese language. Cultural documents in Vietnamese alphabet were published and popularized significantly, which is the phase of pre-modern Vietnamese language. Besides, the exposure to French and French culture triggered the establishment of Vietnam press and modern prose in Vietnamese alphabet. The victory of August Revolution contributed in bringing throne to Vietnamese language. Then, Vietnamese grew rapidly and comprehensively with profound influence on minority languages in Vietnam. This presents the phase of modern Vietnam language that Vietnamese people use today.