Mekong Delta geography takes an important implication for the development of whole region. Located in a prime location, Mekong Delta simultaneously holds a strategic position of the country.
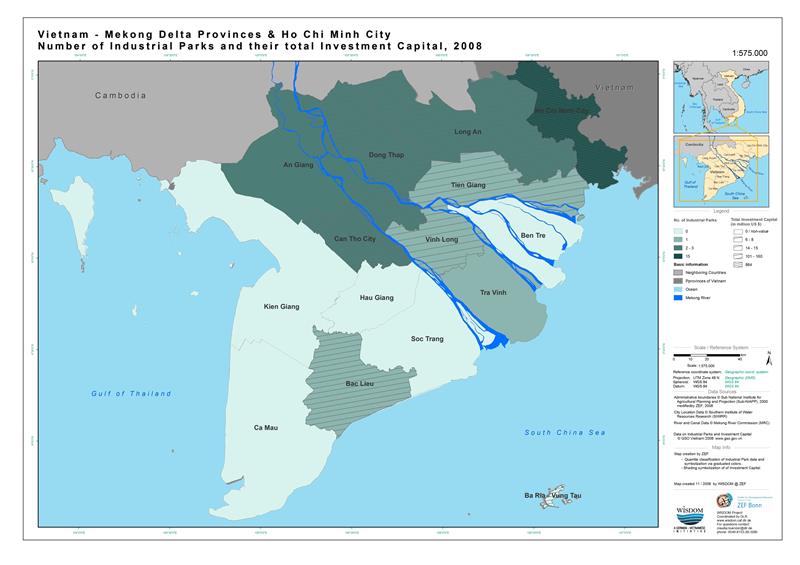
Mekong Delta accounts for a large area of Vietnam geopgraphy. It consists of a central municipality – Can Tho and 12 provinces, namely Long An, Tien Giang, Ben Tre, Vinh Long, Tra Vinh, Soc Trang, Bac Lieu, Ca Mau, Kien Giang, An Giang, Dong Thap, Hau Giang with a total natural area of 39,734 sqkm, accounting for 12.2% of the country's natural area.
Geographical location
Poles of the plain in the mainland include the west one at 106° 26' (My Duc commune, Ha Tien town, Kien Giang), the east one at 106°48' (Tan Dien commune, Go Cong Dong district, Tien Giang), the north one at 11°1' (Loc Giang commune, Duc Hoa district, Long An) and the south one at 8°33' (Dat Mui, Ngoc Hien District, Ca Mau).
As the southern region in Vietnam, Mekong Delta geography is adjacent Southeastern region, with Cambodia to the north, with Gulf of Thailand to the southwest, and with South China Sea to the southeast. In addition, located at the end of Indochina peninsula, adjacent the southern key economic zone, Mekong Delta owns the close and important two-way relationship. Situated adjacent Cambodia and common Mekong River, the region offers favorable conditions to exchange and cooperate with other countries on the peninsula. Besides, located in the end of the country’s southwest with 73.2 km long coastline and islands, such as Tho Chu Island, Phu Quoc Island - exclusive economic zones bordering South China Sea and Gulf of Thailand, Mekong Delta owns tourism potentials need explored. Furthermore, the region belongs to the region of maritime transportation, international air transport between South Asia and Southeast Asia as well as Australia and other islands in Pacific. This position plays an extremely important role in international exchanges.
Terrain

Mekong Delta of Vietnam was formed from alluvial sediments and the accretion through eras of sea level change. Mixture activities of the river and sea has formed fertile alluvial soils along the riverside dikes and coastal acid sulphate soils on low-lying sediments as Plain of Reeds, Long Xuyen - Ha Tien quadrilaterals, Hau River southwest side, and Ca Mau peninsula. The Mekong Delra topography thus is relatively flat with an average height of 3 - 5m above the sea level.
Land
The area of land in Mekong Delta includes the following groups:
+ Alluvial soil: Mainly concentrate in coastal areas of Tien and Hau River system with an area of 1.2 million hectares, accounting for 29.7% of the region's natural land area and about 1/3 of whole country’s alluvial soil area. This soil group owns a high fertility, which is suitable for rice crops, fruit trees, and short-term industrial trees.
+ Alkaline soil: Concentrate in Plain of Reeds, Ha Tien, and the valley of Ca Mau peninsula center with a total area of 1.2 million hectares, accounting for 40% of the whole area. The soil’s characteristic is the high toxin level and weak mechanical property.
+ Acrisols: Owning area of over 134,000 hectares, accounting for 3.4 % of the whole area, this soil group mainly concentrates along Cambodian border and on the shelves of ancient silt in Plain of Reeds. The soil is fairly lightweight, porous, low fertility, and normal toxicity level.
In addition, there are also some other soil groups such as sandy soil, peat, barren soil, or erosion soil...occupying a small area of approximately 0.9% of the whole area. In general, the land here is very favorable for agricultural development, proper rice, coconut, sugarcane, pineapple, and fruit trees.
Water Resources

With a downstream system of Mekong River in Vietnam, total water volume of Mekong River is about 500 billion cubic meter, of which, there is 79% of Tien River and Hau River accounts for 21%. Additionally, the hydrological regime seasonally changes. In rainy season, the water brings much more silt accreting the plain. However, in dry season, water reduction bringing the tide into the plain makes coastal areas be severely affected by salinity.
Marine Resources
Mekong Delta owns 732 km of coastline length with many bays and estuaries. Sea in Mekong Delta contains much precious seafood with high reserves. There are also many islands and archipelagos retaining high economic potential like Tho Chu Island and Phu Quoc. In addition, the coastal is mangrove systems holding many economic and ecological values with the diversified flora and fauna.
Mineral Resources
Mekong Delta is blessed with diverse mineral resources. There are prospects for oil and gas exploitation in continental shelf when the region is adjacent South China Sea and Gulf of Thailand, including sedimentary basins, namely Cuu Long, Nam Con Son and Tho Chu - Malaysia. Additionally, mineral reserve is fairly tremendous with the limestone approximately 130 to 440 million tons, granite and Andesite about 450 million cubic meter, clay reserves up to 40 million cubic meter, the sand and gravel up to 10 million cubic meter per year, the peat about 370 million tons. Mineral water is in Long An, Tien Giang, Vinh Long, Soc Trang, Minh Hai.