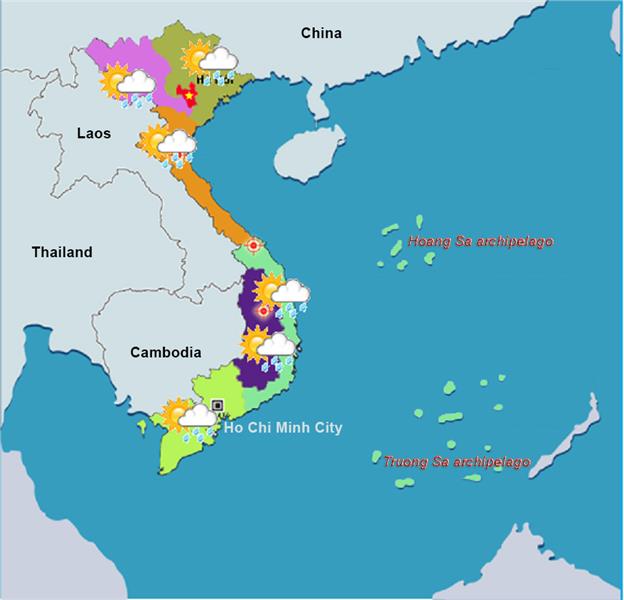
Vietnam weather owns many distinct characteristics from the north to the south. Accordingly, there is a warm humid subtropical climate in North, whereas monsoon tropical climate in Central, and Savanna tropical climate in South and Central Highlands.
Vietnam geography completely lies on a tropical zone, yet its climate is divided into 3 distinct areas according to Koppen climate classification with a warm humid subtropical climate in North, monsoon tropical climate in Central, and Savanna tropical climate in South and Central Highlands. Simultaneous, due to its location in the southeastern edge of Asia, bordering South China Sea (part of Pacific Ocean), Vietnam weather is directly influenced of the trade monsoon climate patterns, usually blowing in low latitude regions.
Northern climate
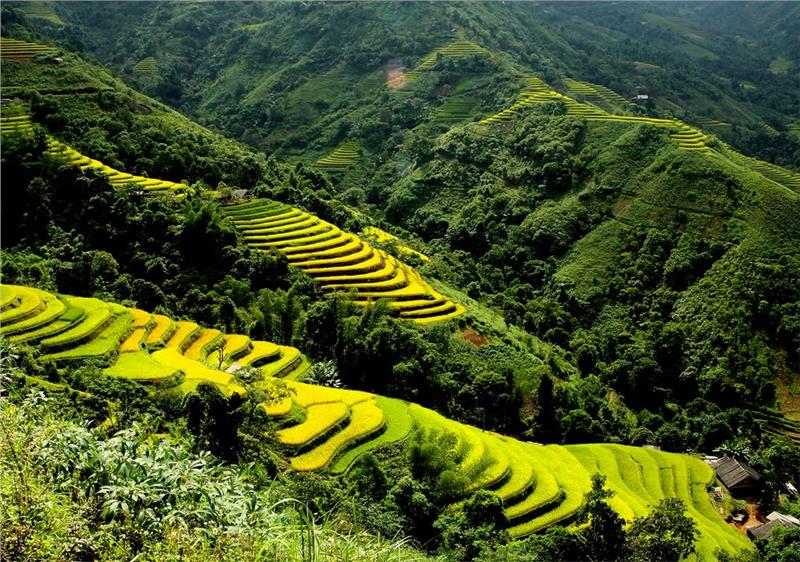

Terrain includes the territory in the north of Hoanh Son range, Northern Northeast and Northern Northwest. Northern temperature is relatively high and humid, climate background is influenced by Chinese continent and brings continental climate; meanwhile, a part of the coastal area is affected by the humid subtropical climate and the monsoon from the mainland.
The whole region owns a humid subtropical climate around year with four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn and winter. At the same time, being influenced by the northeast and southeast monsoon, the annual average temperature gradually increases from the north to the south. It is a typical characteristic of the North delta and the coast. Northern Vietnam weather in summer from May to September is hot and humid whereas it is cold, dry, and drizzly in the winter from October to April. The annual average temperature is about 25°C and the average rainfall is from 1,700 to 2,400 mm. The lowest temperature in the winter is usually in December and January. At that time in the northern mountainous area (such as Sapa, Tam Dao and Hoang Lien Son), the temperature might be lower than 0°C, appearing the icy and snow possibly.
Weather in Northern Vietnam often suffers lots of bad effects of the weather. There are annual 6 to 10 hurricanes and tropical depressions, causing flooding and directly threatening the life and agriculture of localities in whole region.
Southern climate
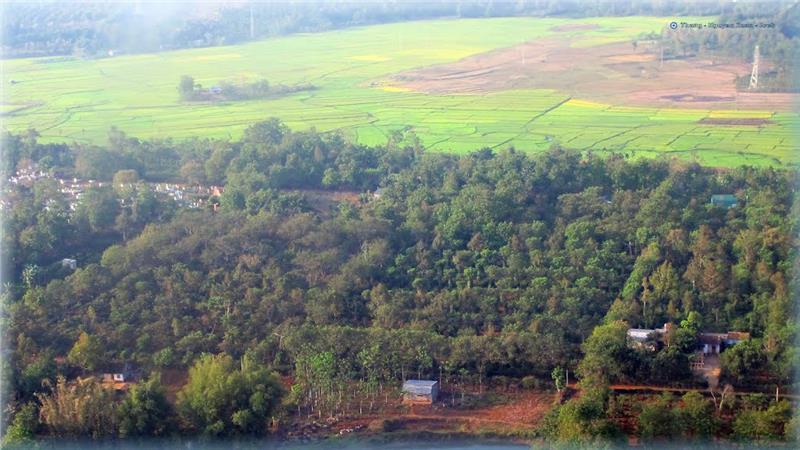

Terrain includes part of the territory in the Central Highlands and the South. This region retains Savanna tropical climate with two seasons, namely the dry season and the rainy season (from April - May to October - November). The region’s temperature is quite high around year; however, Southern Vietnam weather is still fairly stable.
Central climate
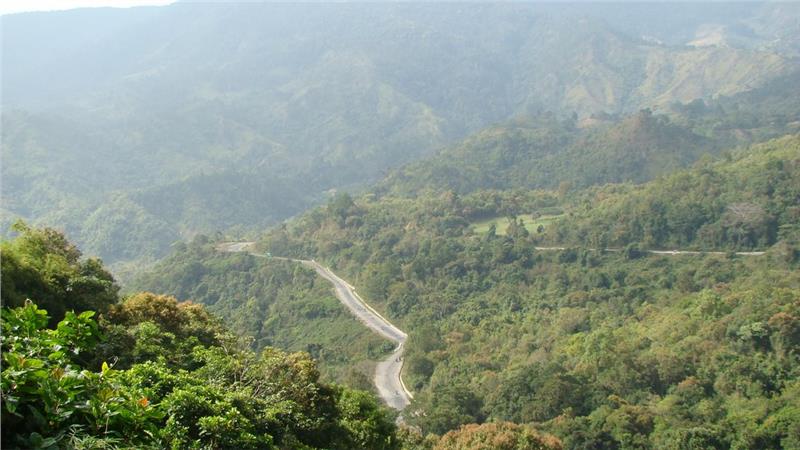

Terrain includes the territory in the east of Truong Son range and stretches from the south of Hoanh Son to Phan Thiet. Central Vietnam weather is a transitional weather region between two above-mentioned regions and characterized by a tropical monsoon climate. This region can be divided into two areas:
North Central is the region in the north of Hai Van Pass. North Central climate is sometimes cold or extremely hot and dry as a result of southwestern wind. The region’s terrain runs along South China Sea coast in Northwest - Southeast direction and directly faces Northeast monsoon mainstream direction. In addition, surrounded by relatively high Truong Son mountain range in the west (at Phong Nha - Ke Bang range) and the south (at Hai Van Pass on Bach Ma range) at the end of the Northeast monsoon, this region is affected by cold weather due to the Northeast monsoon, along with much rainy (especially in Thua Thien - Hue). In the summer the Southwest monsoon strongly blows from the Gulf of Thailand across the vast continent to Truong Son range, the weather is often hot and dry (sometimes up to > 40°C and the relative humidity about 50 ÷ 60). This wind also called “foehn” wind.
South Central Coast is a South Central coastal plain in the north of Hai Van Pass. Fairly similar to Hai Van Pass; however, South Central Coast temperature is quite higher and there is occasionally a winter with a short period of the cold. Additionally, effects of hot and dry western wind are not as strong as in North Central.
An important feature of this region is that dry and rainy seasons here are not the same time point as 2 seasons of the rest regions. In the summer, while whole country is provided with the highest rainfall, the climate of this region is in the driest period.
Northwestern climate – climate in mountainous area
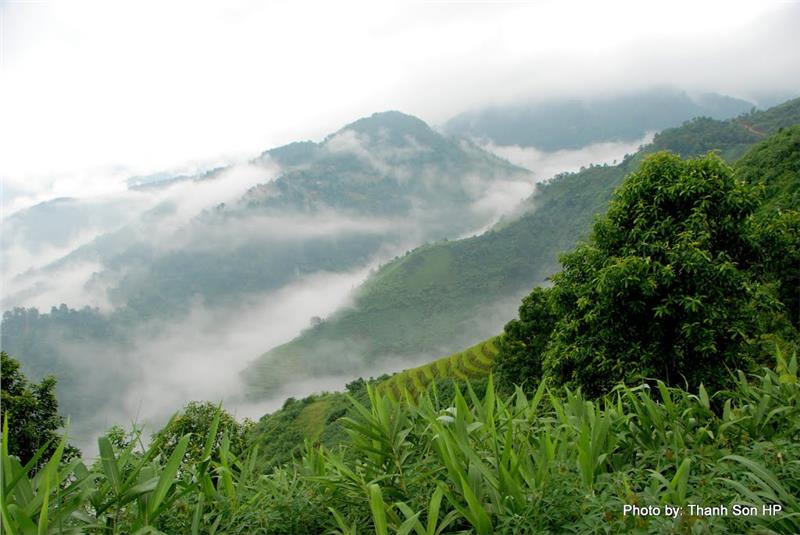

Northwest in Northern Vietnam is a region consisting mainly of medium and alpine mountains. The most voluminous and highest mountain range is Hoang Lien Son with many mounts peaking over 2500m high, especially the tallest one, Fansipan Mountain with 3143 meters. With this type of topography, Northwestern Vietnam weather is described by tropical climate influenced by monsoon. Monsoon regimes are different from time to time. In the summer the southwest monsoon makes weather in the region hot and dry with heavy rains; meanwhile, in the winter the northeast monsoon brings cold, dry, and less rainy weather. The wind regime creates a somewhat harsh weather, causing dry heat, drought, and frost, which hinders local production and daily life. Northwestern Vietnam climate witnesses a small fluctuation in the condition of weather; it is relatively cool all year round. In wet season, you can have a chance to see an extreme of snow or flurry in December and January in Sapa. During this time, the weather is much colder than that in the northeast part. The temperature may be under 100C for long period.