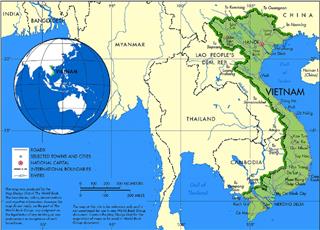
Situated in the prime location, Vietnam area and border keeps an important role in the development of economy, politics, and culture among countries in the region in particular and over the world in general.
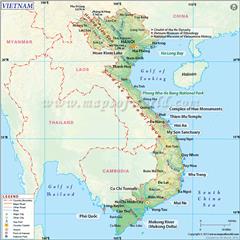
Vietnam has an area of 331,212 square kilometers, including about 327,480 square kilometers of land and over 4,200 square kilometers of inland sea with more than 2,800 islands, reefs in abundant shapes, near and far shore, including the Spratly and Paracel Islands belonging to Vietnam's sovereignty. In addition, Vietnam geography owns internal waters, territorial waters, exclusive economic zone (EEZ) and a continental shelf identified large nearly three times than the land area with over 1 million square kilometers.
Total of whole country area: 331,212 square kilometers
• Land: about 324,480 square kilometers
• Inland waters: more than 4,200 square kilometers
Length of land border
• Total: 4,639 kilometers
• Country border: Cambodia (1,228 kilometers), China (1,281 kilometers), Laos (2,130 kilometers)
Coastline
• 3,260 kilometers (not counting islands)
Waters under the sovereignty and jurisdiction
• The territorial waters: 12 nautical miles (22 kilometers) from the baseline
• Territorial waters contiguous zone: 12 nautical miles (22 kilometers) from the territorial waters.
• Exclusive economic zone: 200 nautical miles (370 kilometers) from the baseline
• Continental Shelf
Altitude
• The lowest point: South China Sea surface (0 m)
• The highest point: Fansipan peak (3,143 meters)
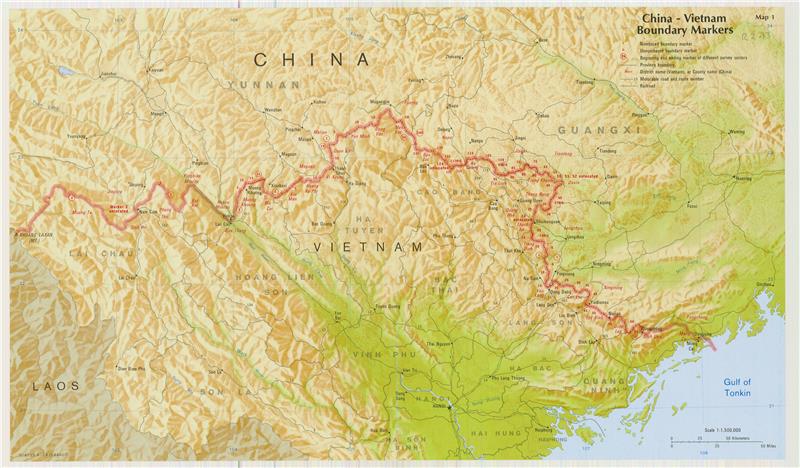
Vietnam border with Laos is specified based on ethnic basis, between rulers of Vietnam and Laos in the mid-17th century. It has been formally defined by a demarcation treaty signed in 1977 and ratified in 1986. Border with Cambodia is determined from the merger of western Mekong Delta in 1867, which has remained virtually unchanged. Borders on land and waters with China are outlined according to the French - Qing treaty in 1887 and 1895, the “borderline” that Vietnam and the People's Republic of China has agreed to respect in 1957-1958. However, Vietnam and China have conflicts relating to land and islands sovereignty from February 1979 up to now, after Vietnam-China border War in 1979. Accordingly, Republic of China (Taiwan), People's Republic of China and Vietnam have been currently claiming sovereignty over Paracel Islands and the problem has been still unresolved (Paracel Islands belong to Vietnam’s sovereignty). In addition, at Spratly Islands, apart from Vietnam, there are five other countries remaining claiming its sovereignty, namely Republic of China (Taiwan), People's Republic of China, Philippines, Malaysia and Brunei (Spratly Islands belong to Vietnam’s sovereignty).
Pole points
The northernmost point: located on the mainland of Vietnam lies on Lung Cu Commune, Dong Van District, Ha Giang Province at coordinates of 23.391185°N 105.323524°E.
The southernmost point: on land located at Rach Tau Cape, Ngoc Hien District, Ca Mau Province at coordinates of 8.562035°N 104.836335°E.

The westernmost point: on the mainland lies on A Pa Chai - Ta Mieu (Sin Thau Commune, Muong Nhe District, Dien Bien Province) (Vietnam - China - Laos border junction) at coordinates of 22.397745°N 102.143297°E .
Easternmost point: on land located at Doi Cape on Hon Gom peninsula, Van Phong Bay, Thanh Van Commune, Van Ninh District, Khanh Hoa Province at coordinates of 12.38941°N 109.27899°E.
If including Spratly Islands, the easternmost point of Vietnam (currently controls) located at Tien Nu (Stone Maiden) Islands at coordinates of 8.855°N 114.655°E.