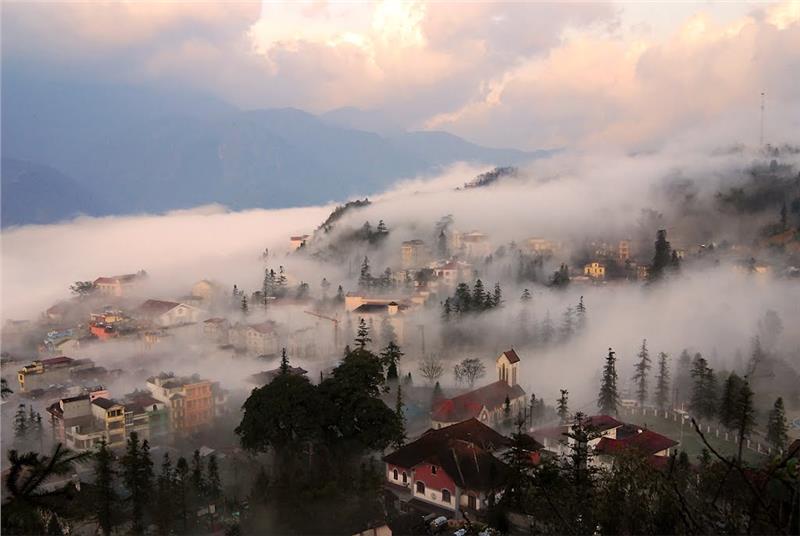
Having picturesque natural landscapes with majestic mountainous areas and green forests, Sapa geography has brought the land the large number of profits thanks to the favorable conditions that it brings for tourism.
Area: 67.864 ha
Administration (Communes/ Town): Sapa Town, Hau Thao, Ban Phung, Ta Phin, Nam Sai, Thanh Phu, Sa Pa, Lao Chai, Trung Chai, San Sa Ho, Thanh Kim, Ban Ho, Su Pan, Suoi Thau, Ta Van, Ban Khoang, Ta Giang Phinh, and Nam Cang
Sapa geographical position
Located in the west of Lao Cai province, Sapa has the geographical coordinates from 22°07'04'' to 22°28'46'' north latitude and from 103°43'28 to 104°04’15’’ east longitude. Sapa district borders with Bat Xat district in the north, Phong Tho, and Than Uyen (Lai Chau) district in the west, Van Ban district in the south, and Bao Thang district and Lao Cai city in the east.
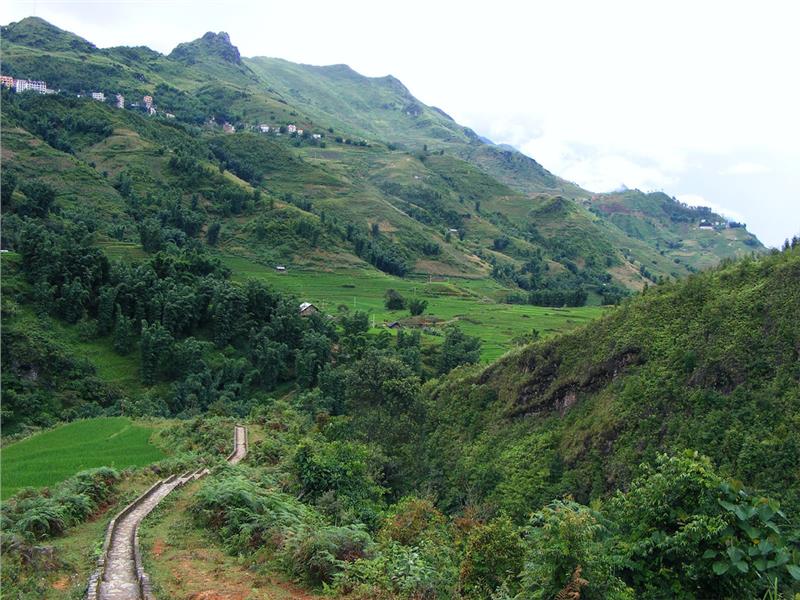

Sapa terrain
Sapa has the average elevation from 1,200 m to 1,800 m. The topography of Sapa gradually inclines in the direction from the west and southwest to the northeast. The highest point of Sapa is Fansipan Mountain with the altitude of 3,143 meters and the lowest point is Bo spring having 400 meters in height. Sapa terrain has the typical features of the North West Vietnam geography. It can be divided into the following three types. Subalpine zone comprises of some communes including Ta Giang Phinh, Ban Khoang, Ta Phin and San Sa Ho. The total area of subalpine zone is 16,574 ha accounted for 24.42% of the natural area of Sapa district. The average height is from 1,400 to 1,700 meters. The rugged terrain is strongly dissected having steep slopes and narrow valleys.
Sapa – Sa Pa sub-regions include 6 communes (Sa Pa, Trung Chai, Lao Chai, Hau Thao, Ta Van, Su Pan) and Sapa Town. The area of this region is 20,170 ha accounted for 29.72% of the whole area. It has the average altitude of 1,500 meters. In general, the topography is less dissected. The strongly dissected sub-regions consist of 7 southern communes (Ban Phung, Nam Sai, Thanh Kim, Suoi Thau, Thanh Phu, Nam Cang and Ban Ho). The total area is 31,120 ha which accounts for 45.86% of Sapa area. The typical features of the strongly dissected sub-regions are sharp peaks, steep slopes, and deep and narrow valleys.
Sapa weather

Sapa has the subtropical climate as the other places in North West Vietnam, but the district has the cool weather all around year due to lying at the high altitude. The land has the cold temperate climate with two distinct seasons. Summers last from May to October with the cool and rainy climate. Winters last from November to April having the cold and dry weather. Especially, Sapa climate has features of 4 seasons in only one day. Due to the influence of the fragmented topography and the special geographical position, Sapa weather has the following basic features:
Temperature: The annual average temperature is 15.4°C. In details, the number reaches 18 - 20°C in summer and 10 - 12°C in winter. April is the hottest time in a year. Besides, the lowest temperature often happens in January with 0oC, sometimes -3.2oC. Nonetheless, Sapa has three types of terrain creating different ecological zones and temperature in different regions.
Sunshine hours: The average sunshine hours fluctuate from 1400 to 1460 hours per year. Sunny days are not evenly distributed among months. In fact, the sunshine hours in summer are larger than in winter. There are about 180 - 200 sunshine hours in April and only 30 - 40 hours in October.
Humidity: The average relative humidity of air is 85 - 90% per year. The lowest humidity reaches 65 - 75 % in April. Besides, the leeward valleys have the more humid climate than other regions of Sapa because of having dense fog in high altitude.
Rainfall: The annual average rainfall is 2,762mm with the highest number of 3,484mm. The rainfall is also unevenly distributed among months. The rainy seasons start from May to October accounted for 80% the total rainfall in one year. In contrast, the dry months have only 50 to 100 mm per month.
Wind: Sapa has two main wind directions including the west and northwest winds in summer and the north and the northeast wind in winter. Due to having the complex mountainous terrain and lying in deep inland position, Sapa is less influenced by monsoon winds. The region is mainly affected by local winds with the average wind speed of 2.2 m/s and up to 19.7 m/s for the strongest one. In addition, Sapa district is also influenced by O Qui Ho wind (a local wind in Sapa) appearing in February, March and April. O Qui Ho wind often brings the hot and cold climate to the land.
Storm: In Sapa, storms often occur in summer and accompanied with heavy rains, floods, and flash floods in the high and steep terrains.
Fog: Fog are a popular phenomenon in Sapa, especially in winter. In freezing periods and in sheltered valleys, frost, ice and snow are often occurred. This period often lasts 2 - 3 days adversely affecting agricultural and forestry production.
Sapa hydrology
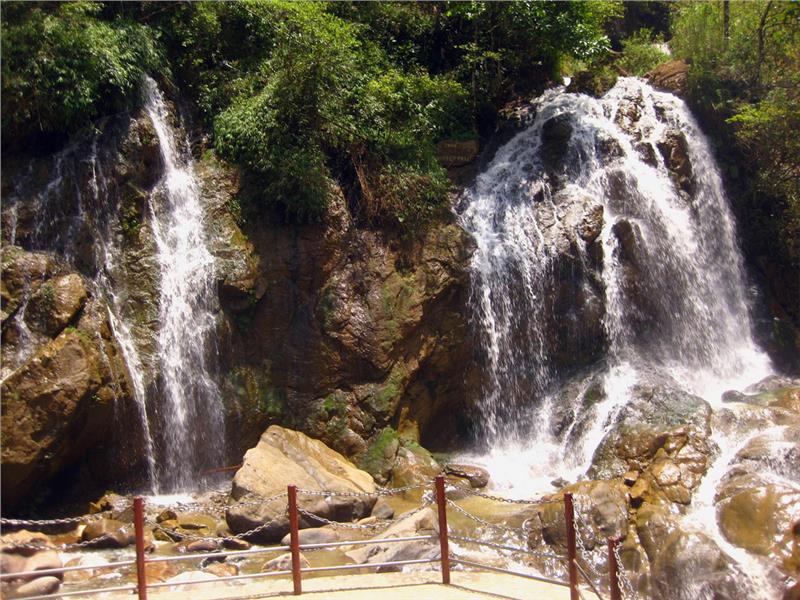

Sapa has a dense network of rivers and streams with two major stream systems including Dum stream and Bo stream. Dum stream has the total length of 50 km derived from the north of Hoang Lien Son mountain range. Dum stream is divided into two main branches and distributed in almost the north and northeast communes such as Sa Pa, Trung Chai, and Ta Phin with the total area of 156 km2. Bo stream system has the length of 80 km originated from the south mountains of Hoang Lien Son with the total area of 578 km2. In general, almost Sapa streams are narrow and sloping having the erratic water flow and seasonal variations. In the rainy season, large floods with strong water flows (989m/s in Bo stream) often happen which may cause flash floods, especially in low terrains. In the dry season, the streams are often shallow.